Numerical Recipes
Table of Contents
Armadillo test
#include <iostream> #include <armadillo> using namespace std; using namespace arma; int main() { mat m = randn<mat>(4, 5); cout << m << endl; return 0; }
Random number generation
Box method Sampling
Algorithm
- Let the distribution to generate be

 is defined in the range
is defined in the range ![$[a, b]$](../../assets/latex/numerical_recipes_c9a1e8df376ecb942b106e02d3e6d1b417da2600.png)
- Find a number
 such that
such that ![$y_m > \underset{x \in [a, b]}{\max} f(x)$](../../assets/latex/numerical_recipes_2e589d1f038fb672d0a05c0916279d22bd52db1a.png)
- Generate a random number

- Convert to random number in the range
![$[a, b]$](../../assets/latex/numerical_recipes_c9a1e8df376ecb942b106e02d3e6d1b417da2600.png) by the letting
by the letting 
- Compute the value
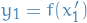
- Generate random number

- Obtain random number in the range
![$[0, y_m]$](../../assets/latex/numerical_recipes_99569540641e569bc94fc56d5ed4233735f655ca.png) by computing
by computing 
- Perform the test:
if( y_2 < y_1)- If
true: return
- If
false: discard and go back to step 4
and go back to step 4
- If
- Repeat steps above until the wanted number of random values have been obtain.
Basically, we end up drawing random numbers in a rectangle box and ONLY keeping the numbers which are under the curve of  .
.

Code
Main code - C++
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES #include <math.h> #include <iostream> #include <armadillo> #include <thread> #include <fstream> using namespace std; using namespace arma; /** * Finds the maximum of the function using coordinate ascent. */ template <typename F> double find_max(F&& f, Col<double> initial, Col<double> x_min = Col<double>{}, Col<double> x_max = Col<double>{}, bool use_xlim = false, double alpha = 0.05) { if (use_xlim) { if (x_min.n_elem != initial.n_elem || x_max.n_elem != initial.n_elem) { throw "different dimensions for initial values and limits for x"; } else if (x_min.n_elem != x_max.n_elem) { throw "different dimensions for x_min and x_max"; } } Col<double> res = vec(initial); double x_curr, x_next; double y_curr, y_next; double x_l, x_r; double y_l, y_r; uword i; do { // iterate through each dimension and see if we can obtain a greater y for (i = 0; i < res.n_elem; ++i) { if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } x_curr = res[i]; y_curr = f(res); // candidate x's x_l = x_curr - alpha; x_r = x_curr + alpha; // compute candidate y's res[i] = x_l; if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } y_l = f(res); res[i] = x_r; if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } y_r = f(res); // check if best candidate y is better x_next = y_l < y_r ? x_r : x_l; res[i] = x_next; y_next = f(res); if (y_next <= y_curr) { // new y is worse => reset to old x res[i] = x_curr; } } // output // cout << y_curr << endl; } while(y_next > y_curr); return f(res); } void test_find_max() { double maximum = 100; Col<double> a = randu<Col<double>>(1); const auto f = [&maximum](Col<double> v) -> double { if (abs(sum(v)) > maximum) { return maximum; } else { return abs(sum(v)); } }; // trying out `find_max` double y_m = find_max(f, a); cout << "Maximum: " << y_m << endl; } /** INTEGRATION METHODS */ enum SAMPLING_METHOD { BOX_METHOD = 0 }; template <typename F, uint N> struct IntegrationArgs { F&& f; uint num_samples; int n_jobs; SAMPLING_METHOD sampling_method; // sampling_method to use for integration Col<double> x_min; Col<double> x_max; double y_m; // at least the maximum of the function being passed bool save = false; // specifies whether or not to save the xs and ys IntegrationArgs(F&& func) : f(func) { } }; /** * Wrapper to enable type-deduction for the `IntegrationArgs`. * * https://stackoverflow.com/a/797632 */ template <uint N, typename F> IntegrationArgs<F, N> integration_args(F&& func, Col<double> x_min, Col<double> x_max, double y_max = 0, bool auto_find_max = false, SAMPLING_METHOD sampling_method = BOX_METHOD, int n_jobs = 1, bool save = false) { auto args = IntegrationArgs<F, N>(func); args.x_min = x_min; args.x_max = x_max; args.num_samples = N; args.sampling_method = sampling_method; args.n_jobs = n_jobs; args.save = save; if (auto_find_max) { // create an starting-point for finding the maximum value of the function in this domain Col<double> initial = randu<Col<double>>(x_min.n_elem); // U(0, 1) initial %= (x_min - x_max); // U(0, b - a) initial += x_max; // U(a, b) = a + U(0, b - a) cout << initial << endl; args.y_m = find_max(func, initial) + 0.05; // adding an extra constant for good measure } else { args.y_m = y_max; } // return IntegrationArgs<F, N>(func, x_min, x_max, y_max, find_max, sample_method, n_jobs); return args; } template <uint N, typename F> IntegrationArgs<F, N> integration_args(F&& func, Col<double> x_min, Col<double> x_max, SAMPLING_METHOD sampling_method = BOX_METHOD, int n_jobs = 1) { return integration_args<N, F>(func, x_min, x_max, 0, true, sampling_method, n_jobs); } template <uint N, typename F> IntegrationArgs<F, N> integration_args_persist(F&& func, Col<double> x_min, Col<double> x_max, SAMPLING_METHOD sampling_method = BOX_METHOD, int n_jobs = 1) { auto a = integration_args<N, F>(func, x_min, x_max, 0, true, sampling_method, n_jobs); a.save = true; return a; } template <uint N, typename F> ostream& dump(ostream &o, const IntegrationArgs<F, N>& args) { o << "Integration arguments:" << endl; o << "Domain:\n" << args.x_min << " " << args.x_max << endl; o << "Num samples: " << args.num_samples << endl; return o; } /** * Samples from UNDER a function using the "box sampling_method". */ template <typename F, uint K> Col<double> _box_method_sampling(IntegrationArgs<F, K> args) { Col<double> a = args.x_min; Col<double> b = args.x_max; double y_m = args.y_m; Col<double> x_1; double y_1; double y_2; uint N = 1000; Col<double> results = zeros(N); uint i; for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { do { x_1 = a + (b - a) % randu<vec>(size(a)); // draw new random input y_1 = args.f(x_1); // compute f(x) y_2 = randu() * y_m; // comparison value } while (y_2 >= y_1); // keep going until we have a valid value results[i] = y_1; } return results; } /** * Using samples from UNDER the function, compute the integral using the Riemann sum. */ template <typename F, uint N> double monte_carlo_integration(IntegrationArgs<F, N> args) { Col<double> a = args.x_min; Col<double> b = args.x_max; Col<double> range = b - a; double y_m = args.y_m; cout << "Maximum value for f used in integration: " << y_m << endl; Col<double> x_1; double y_1; double y_2; dump(cout, args); uint inside = 0; uint i; if (args.save) { Mat<double> out_x_1 = zeros(N); Col<double> out_y_1 = zeros(N); Col<double> out_y_2 = zeros(N); for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { x_1 = a + range % randu<Col<double>>(size(a)); // draw new random input y_1 = args.f(x_1); // compute f(x) y_2 = randu() * y_m; // comparison value if (y_2 < y_1) { inside++; } // store values out_x_1[i] = x_1[0]; out_y_1[i] = y_1; out_y_2[i] = y_2; } out_x_1.save("x_1.txt", csv_ascii); out_y_1.save("y_1.txt", csv_ascii); out_y_2.save("y_2.txt", csv_ascii); } else { for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) { x_1 = a + range % randu<Col<double>>(size(a)); // draw new random input y_1 = args.f(x_1); // compute f(x) y_2 = randu() * y_m; // comparison value if (y_2 < y_1) inside++; } } cout << "Range: " << range << endl; double ratio = ((double)inside) / N; cout << "Monte Carlo integration: [" << inside << " / " << N << "] " << ratio << endl; // compute area of box Col<double> diff = b - a; // this is just a `reduce`, since an actual `reduce` is only available from C++17 double tot = y_m; // "height" std::for_each(std::begin(diff), std::end(diff), [&tot](double v) { tot *= v; // "widths" }); cout << "Box 'volume': " << tot << endl; return ratio * tot; } /** * Wrapper around multiple sampling_method of integration, which is specified in the `args`. */ template <typename F, uint N> Col<double> integrate(IntegrationArgs<F, N> args) { switch (args.sampling_method) { case BOX_METHOD: { return Col<double>{monte_carlo_integration(args)}; } default: throw "invalid sampling_method of integration specified"; } } /** END INTEGRATION METHODS */ /** Gaussian distribution */ class MyGaussian { public: Col<double> mu; Mat<double> sigma; //! Default constructor MyGaussian(Col<double> mean, Mat<double> variance) : mu(mean), sigma(variance) { _sigma_det = det(variance); _sigma_inv = inv(variance); }; double evaluate(Col<double> x); double integralAnalytic(); template <uint N> Col<double> integralNumeric(); protected: private: // to not have to recompute these each time double _sigma_det; Mat<double> _sigma_inv; double _domain_width = 10; // can't integrate to and from infinity }; double MyGaussian::evaluate(Col<double> x) { Col<double> diff = this->mu - x; // apparently we're not supposed the normalization constant... // double z = 1.0 / sqrt(2 * M_PI * this->_sigma_det); // return (z * exp(- 0.5 * diff.t() * this->_sigma_inv * diff))[0]; return exp(- 0.5 * diff.t() * this->_sigma_inv * diff)[0]; } template <uint N> Col<double> MyGaussian::integralNumeric() { auto f = [&](Col<double> x) { return this->evaluate(x); }; const auto job_args = integration_args<N>(f, this->mu - this->_domain_width * this->_sigma_det, this->mu + this->_domain_width * this->_sigma_det, BOX_METHOD); return integrate(job_args); } double MyGaussian::integralAnalytic() { // assuming we're integrating from -\infty to \infty return (this->_sigma_det) * sqrt(2 * M_PI); } /** * Simple test for the `MyGaussian` class */ void test_my_gaussian() { Col<double> mu = zeros(1); Mat<double> sigma = eye(1, 1); auto g = new MyGaussian(mu, sigma); cout << "Gaussian parameters: " << "mu = " << g->mu << "sigma = " << g->sigma << endl; auto numerical = g->integralNumeric<10000>(); cout << "f(x) = " << g->evaluate(zeros(1)) << endl << "Numerical integration: " << numerical[0] << endl << "Size of numerical integration " << size(numerical) << endl << "Analytical integration: " << g->integralAnalytic() << endl; } /** END MyGaussian */ int main() { test_find_max(); // the Gaussian stuff test_my_gaussian(); // // setup for parallel Monte-Carlo integration // const int N = 100000000; // const int n_jobs = 3; // const int n_per_job = N / n_jobs; // const auto job_args = integration_args<n_per_job>(f, x_min, x_max,BOX_METHOD); // Col<double> runs[n_jobs]; // thread threads[n_jobs]; // int i; // // start jobs // for (i = 0; i < n_jobs; ++i) { // threads[i] = thread([i, &job_args,&runs]() { // runs[i] = integrate(job_args); // }); // } // // gather results // for (i = 0; i < n_jobs; ++i) { // threads[i].join(); // cout << "Integral " << i << ": " << runs[i]; // } return 0; }
Maximum: 100 Gaussian parameters: mu = 0 sigma = 1.0000 4.9904 Maximum value for f used in integration: 1.04995 Integration arguments: Domain: -10.0000 10.0000 Num samples: 10000 Range: 20.0000 Monte Carlo integration: [1199 / 10000] 0.1199 Box 'volume': 20.9991 f(x) = 1 Numerical integration: 2.51779 Size of numerical integration 1x1 Analytical integration: 2.50663
Visualization
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.stats import norm # load data x_1 = np.loadtxt("x_1.txt") y_1 = np.loadtxt("y_1.txt") y_2 = np.loadtxt("y_2.txt") # plot it mask = y_1 > y_2 xs = x_1 xs_true = np.linspace(-10, 10, x_1.shape[0]) ys_true = norm.pdf(xs_true, 0, 1) xs_in = xs[mask] xs_out = xs[~mask] ys_in = y_1[mask] ys_out = y_1[~mask] ratio = y_2[mask].shape[0] / y_2.shape[0] box = np.max(y_1) * (np.max(xs) - np.min(xs)) z = ratio * box # plt.scatter(xs_out, ys_in) # plt.scatter(xs_in, ys_out) plt.scatter(xs[mask], y_2[mask] / z, s=1) plt.scatter(xs[~mask], y_2[~mask] / z, s=1) plt.plot(xs_true, ys_true, label="$\mathcal{N}(0, 1)$") plt.legend() plt.show() print(z)
Bugs
- DONE Apparently I'm drawing examples if they're ON the curve, not UNDER
No. Well yes, but that was because I was drawing all the points where
 , which is NOT what I ought to. The points UNDER the curve is of course
, which is NOT what I ought to. The points UNDER the curve is of course  where
where  is literally values evaluated for
is literally values evaluated for  !
!
- DONE Got the wrong integral
Well, I wasn't. I was of course already divinding by the normalization factor, i.e. the integral, and thus I got the wrong result compared to their unnormalized integral… So the code worked, I just compared with the wrong values.
Checkpoint 1
Code
Main code
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES #include <math.h> #include <iostream> #include <armadillo> #include <fstream> using namespace std; using namespace arma; /** * Finds the maximum of the function using coordinate ascent. */ template <typename F> double find_max(F&& f, Col<double> initial, Col<double> x_min = Col<double>{}, Col<double> x_max = Col<double>{}, bool use_xlim = false, double alpha = 0.05, uword max_steps = 1000) { if (use_xlim) { if (x_min.n_elem != initial.n_elem || x_max.n_elem != initial.n_elem) { throw "different dimensions for initial values and limits for x"; } else if (x_min.n_elem != x_max.n_elem) { throw "different dimensions for x_min and x_max"; } } Col<double> res = vec(initial); double x_curr, x_next; double y_curr, y_next; double x_l, x_r; double y_l, y_r; uword cnt = 0; uword i; do { // iterate through each dimension and see if we can obtain a greater y for (i = 0; i < res.n_elem; ++i) { if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } x_curr = res[i]; y_curr = f(res); // candidate x's x_l = x_curr - alpha; x_r = x_curr + alpha; // compute candidate y's res[i] = x_l; if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } y_l = f(res); res[i] = x_r; if (use_xlim) { if (res[i] < x_min[i]) { res[i] = x_min[i]; } else if (res[i] > x_max[i]) { res[i] = x_max[i]; } } y_r = f(res); // check if best candidate y is better x_next = y_l < y_r ? x_r : x_l; res[i] = x_next; y_next = f(res); if (y_next <= y_curr) { // new y is worse => reset to old x res[i] = x_curr; } } cnt++; // output // cout << y_curr << endl; } while(y_next > y_curr && cnt < max_steps); return f(res); } void test_find_max() { double maximum = 100; Col<double> a = randu<Col<double>>(1); const auto f = [&maximum](Col<double> v) -> double { if (abs(sum(v)) > maximum) { return maximum; } else { return abs(sum(v)); } }; // trying out `find_max` double y_m = find_max(f, a); cout << "Maximum: " << y_m << endl; } /** Sampling */ template <typename F> struct SamplingArgs { F&& f; Col<double> x_min; Col<double> x_max; double y_m; uint n_samples = 1000; int n_jobs = 1; bool save = false; string out_filename = "samples.txt"; SamplingArgs(F&& func) : f(func) { } }; template <typename F> SamplingArgs<F> sampling_args(F&& func, Col<double> x_min, Col<double> x_max, uint n_samples = 1000, bool save = false) { auto a = SamplingArgs<F>(func); a.x_min = x_min; a.x_max = x_max; a.n_samples = n_samples; a.save = save; a.y_m = find_max(a); return a; } template <typename F> double find_max(SamplingArgs<F> arg) { Col<double> initial = randu<Col<double>>(arg.x_min.n_elem); // U(0, 1) initial %= (arg.x_min - arg.x_max); // U(0, b - a) initial += arg.x_max; // U(a, b) = a + U(0, b - a) return find_max(arg.f, initial, arg.x_min, arg.x_max, true, 0.001, 10000) + 0.05; } /** * Samples from UNDER a function using the "box sampling_method". */ template <typename F> Mat<double> box_method_sampling(SamplingArgs<F> args) { Col<double> a = args.x_min; Col<double> b = args.x_max; double y_m = args.y_m; Col<double> x_1; double y_1; double y_2; uint i; uword j; mat result = zeros<mat>(args.n_samples, a.n_elem + 1); // (n, p + 1) for (i = 0; i < args.n_samples; ++i) { do { x_1 = a + (b - a) % randu<vec>(size(a)); // draw new random input y_1 = args.f(x_1); // compute f(x) y_2 = randu() * y_m; // comparison value } while (y_2 >= y_1); // keep going until we have a valid value for (j = 0; j < x_1.n_elem; ++j) { result(i, j) = x_1[j]; } result(i, j) = y_2; } return result; } /** END Sampling */ /** Checkpoint 1 */ double exponential(double lambda, double x) { return lambda * exp(- lambda * x); } void test_exponential(double lambda, uint n) { auto x_min = Col<double>{ 0 }; auto x_max = Col<double>{ 20 }; auto f = [lambda](Col<double> x) { return lambda * exp(- lambda * x[0]); }; auto args = sampling_args(f, x_min, x_max, n, true); args.y_m = 1; args.out_filename = "samples_test.txt"; auto out = box_method_sampling(args); out.save(args.out_filename, raw_ascii); } int main() { // test_find_max(); // sampling from an exponential // test_exponential(1 / 2.2, 1000); double lambda = 1 / 2.2; uint n = 1000 * 500; auto x_min = Col<double>{ 0 }; auto x_max = Col<double>{ 20 }; auto f = [lambda](Col<double> x) { return lambda * exp(- lambda * x[0]); }; auto args = sampling_args(f, x_min, x_max, n, true); cout << "y_m: " << args.y_m << endl; cout << "Sampling..."; auto out = box_method_sampling(args); cout << "OK" << endl; cout << "Saving to file " << args.out_filename << "..."; out.save(args.out_filename, raw_ascii); cout << "OK" << endl; }
ym: 0.504752 Sampling…OK Saving to file samples.txt…OK
Visualization
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
# parameters
n_experiments = 500
n_per_experiment = 1000
# load data
data = np.loadtxt("samples.txt")
runs = data.reshape(-1, n_per_experiment, 2)
means = runs.mean(axis=1)
single_experiment_std = runs[0, :, 0].std()
single_experiment_mean = runs[0, :, 0].mean()
print("Std. error of the mean for single experiment of {} samples: {:.5f} ± {:.5f}".format(
n_per_experiment,
single_experiment_mean,
single_experiment_std / np.sqrt(n_per_experiment)
))
all_experiments_std = means[:, 0].std()
all_experiments_mean = means[:, 0].mean()
print("Std. error of the mean over {} experiments of {} samples: {:.5f} ± {:.5f}".format(
n_experiments,
n_per_experiment,
all_experiments_mean,
all_experiments_std / np.sqrt(n_per_experiment)
))
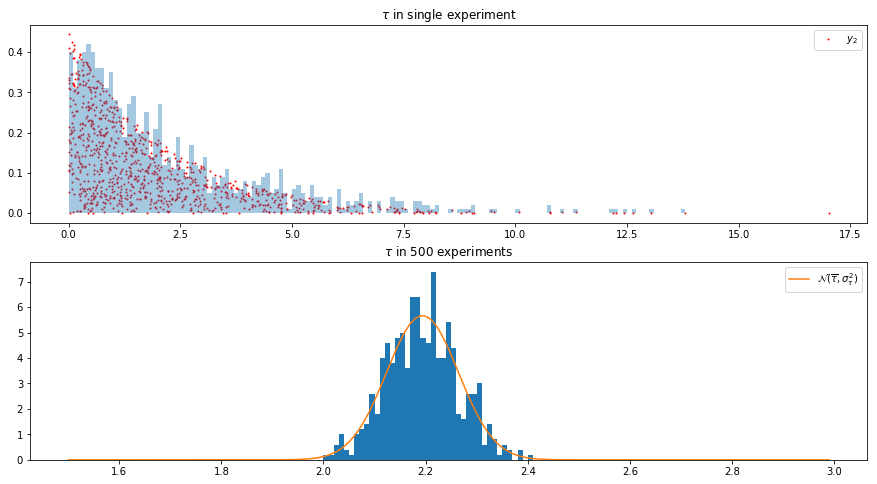
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, figsize=(15, 8))
axes[0].set_title(r"$\tau$ in single experiment")
axes[0].hist(runs[0, :, 0], np.arange(0, 15, 0.1), normed=True, alpha=0.4)
axes[0].scatter(runs[0, :, 0], runs[0, :, 1], s=1, c="r", label="$y_2$")
axes[1].set_title(r"$\tau$ in 500 experiments")
axes[1].hist(means[:, 0], np.arange(1.5, 3, 0.01), normed=True)
xs = np.arange(1.5, 3, 0.01)
axes[1].plot(xs, norm.pdf(xs, loc=all_experiments_mean,
scale=all_experiments_std),
label=r"$\mathcal{N}(\overline{\tau}, \sigma_\tau^2)$")
axes[0].legend()
axes[1].legend()
fig
Questions
How well can you expect to measure the true lifetime from 1 experiment?
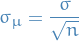
and then

is the std. error of the mean.
How well can you expect to measure the true lifetime from 500 experiments?
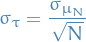
and then

is the std. error of the mean.